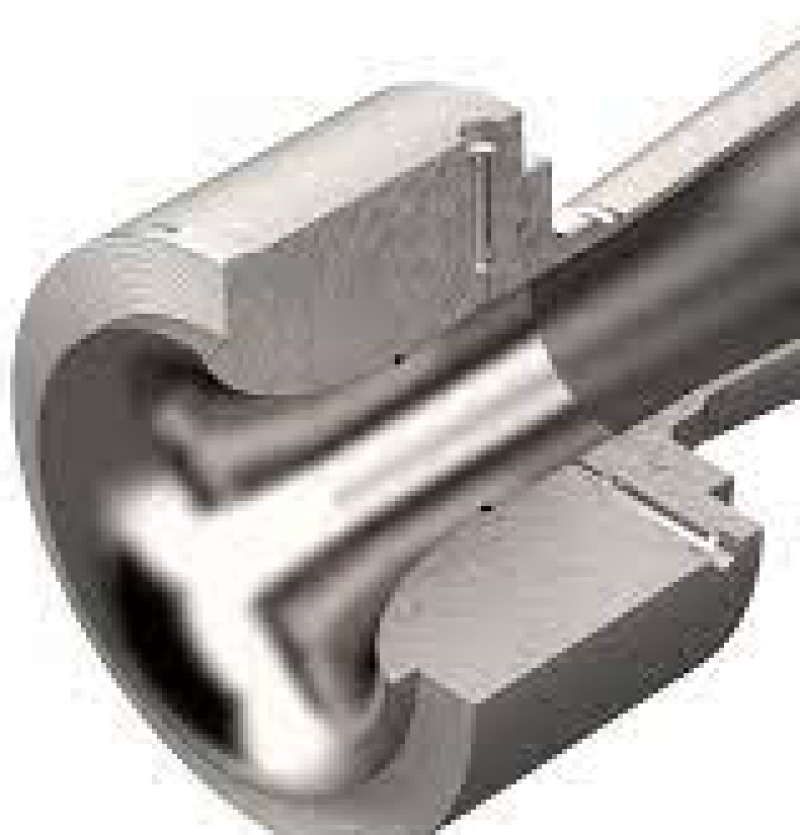
Flow Nozzle
Hits : 4701 |
Flow nozzles are used for flow measurement in various industries. Due to their long documented history, flow nozzle designs and installation requirements are known and recognized by national and international standards organizations. We suggest you to read our next part.
What does a flow nozzle mean?
Flow nozzles are used for flow measurement in various industries. Due to their long documented history, flow nozzle designs and installation requirements are known and recognized by national and international standards organizations.
In head type measurement principles, restrictions are put in the fluid flow path to cause a pressure drop, which is related to the flow rate by applying Bernoulli’s equation. Flow nozzle is a flow element of that kind, similar to orifice plate. The flow nozzle is used for high-velocity flow measurement, where erosion or cavitations would wear or damage an orifice plate. The flow nozzle has a smooth inlet which results in a higher coefficient of discharge than most other differential meters. This means greater flow capacity when compared to most other flow elements in head type flow measurement, of the same size.
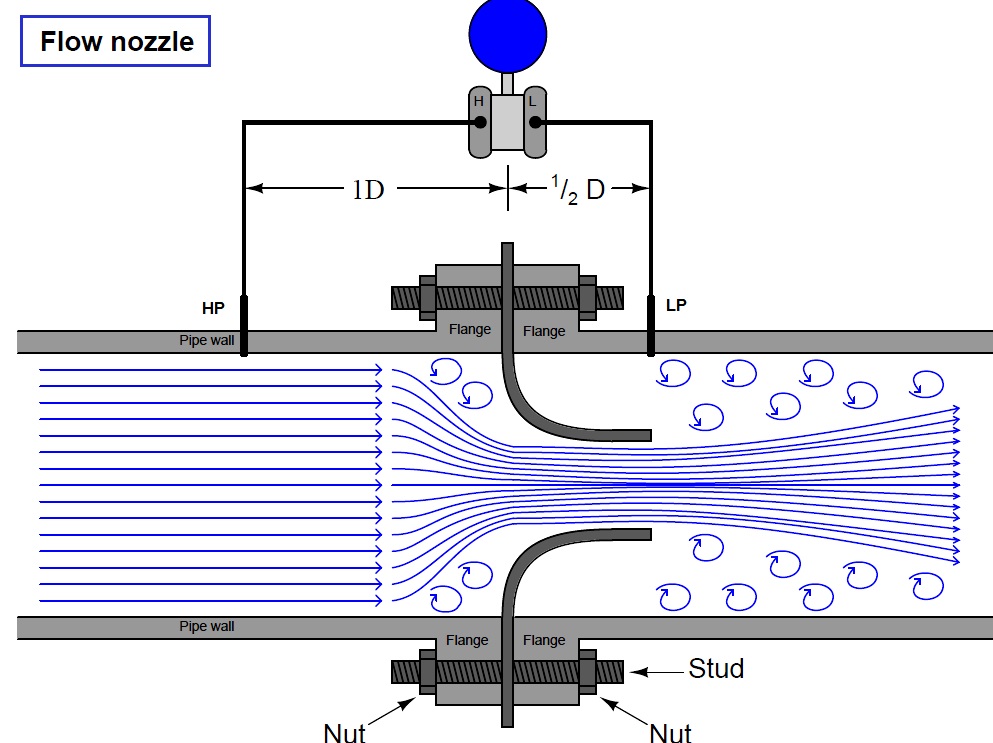
The flow nozzle lies between the orifice plate and the venture tube both in performance and cost. Compared to orifice plates, flow nozzles have a lower pressure drop but are in demand for high-precision manufacturing. Accuracy can be sustained indefinitely since . there are no sharp edges to wear.
Types of Flow Nozzles
From a design point of view, flow nozzles can be classified as:
- ASME MFC-3M flow nozzle
- Long radius
- Short radius;
- ISA 1932 flow nozzle;
- Venturi flow nozzle.
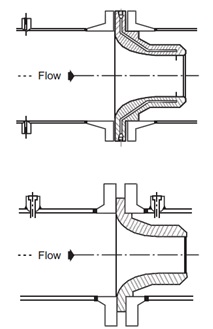
ASME flow nozzle: On account of its smooth rounded design, the ASME flow nozzle not only gives a higher discharge coefficient, it is also more effective for sweeping-through of particles in the flow stream, extending product life by reducing wear and potential damage. ASME flow nozzles follow ASME MFC-3M. ASME nozzles offer ±2% uncertainty of coefficient of discharge. These are used for a beta ratio of 0.2-0.8 in throat with a Reynolds number ranging between (0.1-2.5) × 106.
ISA 1932 Flow nozzle: The ISA 1932 nozzle is suitable for high-velocity, nonviscous, erosive flow, which otherwise would wear or damage an orifice plate. The discharge coefficient of the nozzle is such that for same beta ratios it can measure about 55% higher flow when compared with an orifice plate. Similarly, it requires less straight length.
Venturi nozzle: Venturi nozzles are usually deployed for flow measurements in gases, vapors, and liquids. Normally this is covered by ISO 5167-3:2003. It offers moderate accuracy of <2%. Low-pressure drop is the main characteristic feature of this flow element.
Applications of Flow Nozzles
Nozzles are used mostly for high-velocity, non-viscous, erosive fluid flows. Where erosion or cavitations would wear or damage an orifice plate, flow nozzles are deployed. They have considerable acceptance in certain industries, such as electrical power generation. Standard nozzles are moderately priced
Advantages:
- Widely used for high-pressure high-temperature steam flow measurement (especially in power plant applications)
- Flow measurement for flows with high velocity
- On account of smooth rounded/elliptical input not damaged by accompanying solid particle lesser erosion hence extended product life
- No moving parts hence extended product life
- Flow nozzle profile is inherently robust with minimum maintenance and inspection required;
- No damming effect;
- Much better seep for debris and liquids.
Disadvantages:
- Installations are difficult when compared with orifice plate installations;
- Pressure recovery is less than with a Venturi tube;
Possibility of pressure shock during recovery.

